Page 38 - WINGS OF AGRI-INNOVATIONS
P. 38
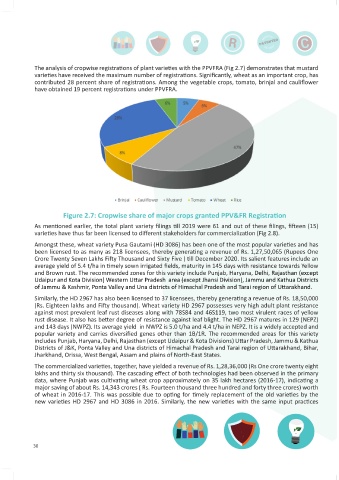
The analysis of cropwise registrations of plant varieties with the PPVFRA (Fig 2.7) demonstrates that mustard were estimated to have saved Rs. 6,680 crores (Rs Six thousand six hundred and eighty crores) in Haryana’s
varieties have received the maximum number of registrations. Significantly, wheat as an important crop, has economy in 2016-17 by replacing the old varieties. In terms of wheat grain production, an estimated 8.8
contributed 28 percent share of registrations. Among the vegetable crops, tomato, brinjal and cauliflower million tonnes of wheat in Punjab and 4.1 million tonnes in Haryana were saved with the adoption of the
have obtained 19 percent registrations under PPVFRA. new wheat varieties HD 3086 and HD 2967, whereas, about 8.8 million tonnes of wheat was potentially lost
by Western UP in 2015-16 owing to poor replacement of old wheat varieties. It is important to note that 13.5
million tonnes of wheat food-grain contributed to the food basket of India in a single year (2016-17) with the
adoption of HD 2967 and HD 3086.
Figure 2.7: Cropwise share of major crops granted PPV&FR Registration
As mentioned earlier, the total plant variety filings till 2019 were 61 and out of these filings, fifteen (15)
varieties have thus far been licensed to different stakeholders for commercialization (Fig 2.8).
Amongst these, wheat variety Pusa Gautami (HD 3086) has been one of the most popular varieties and has Figure 2.8: Status of licensing of various plant varieties
been licensed to as many as 218 licensees, thereby generating a revenue of Rs. 1,27,50,065 (Rupees One
Crore Twenty Seven Lakhs Fifty Thousand and Sixty Five ) till December 2020. Its salient features include an 3.Trademarks
average yield of 5.4 t/ha in timely sown irrigated fields, maturity in 145 days with resistance towards Yellow 8
and Brown rust. The recommended zones for this variety include Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Rajasthan (except Indian trademark law statutorily protects trademarks as per the Trademark Act, 1999 and also under the
Udaipur and Kota Division) Western Uttar Pradesh area (except Jhansi Division), Jammu and Kathua Districts common law remedy of passing off. The objective of the Trademarks Act, 1999 is to register trademarks
of Jammu & Kashmir, Ponta Valley and Una districts of Himachal Pradesh and Tarai region of Uttarakhand. applied for in the country and to provide for better protection of trademark for goods and services and also
to prevent fraudulent use of the mark.
Similarly, the HD 2967 has also been licensed to 37 licensees, thereby generating a revenue of Rs. 18,50,000
(Rs. Eighteen lakhs and Fifty thousand). Wheat variety HD 2967 possesses very high adult plant resistance In 2005, the IARI filed its first trademark i.e. PUSA logo in Class 31, which stands for Raw and unprocessed
against most prevalent leaf rust diseases along with 78S84 and 46S119, two most virulent races of yellow agricultural, aquaculture, horticultural and forestry products; raw and unprocessed grains and seeds; fresh
rust disease. It also has better degree of resistance against leaf blight. The HD 2967 matures in 129 (NEPZ) fruits and vegetables, fresh herbs; natural plants and flowers; bulbs, seedlings and seeds for planting in
and 143 days (NWPZ). Its average yield in NWPZ is 5.0 t/ha and 4.4 t/ha in NEPZ. It is a widely accepted and Indian Trademark Registry. Followed by this, in 2012 a word mark i.e. name ‘PUSA’ was filed by ZTM & BPD
popular variety and carries diversified genes other than 1B/1R. The recommended areas for this variety Unit as a trademark in total eight (8) classes i.e. 1, 5, 7, 8, 29, 30, 31, 32, and got registered in 2018 (Table 2.5).
includes Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Rajasthan (except Udaipur & Kota Divisions) Uttar Pradesh, Jammu & Kathua In 2019, logo of Indian Agricultural Research Institute and word mark ‘PUSA’ were filed at Indian Trademark
Districts of J&K, Ponta Valley and Una districts of Himachal Pradesh and Tarai region of Uttarakhand, Bihar, Registry for accordance of their status as well-known marks (Table 2.6).
Jharkhand, Orissa, West Bengal, Assam and plains of North-East States.
The commercialized varieties, together, have yielded a revenue of Rs. 1,28,36,000 (Rs One crore twenty eight In 2017 the logo and word mark for intellectual property facilitation centre (IPFC) i.e. IP Spectra were filed in
lakhs and thirty six thousand). The cascading effect of both technologies had been observed in the primary
data, where Punjab was cultivating wheat crop approximately on 35 lakh hectares (2016-17), indicating a
major saving of about Rs. 14,343 crores ( Rs. Fourteen thousand three hundred and forty three crores) worth
of wheat in 2016-17. This was possible due to opting for timely replacement of the old varieties by the
new varieties HD 2967 and HD 3086 in 2016. Similarly, the new varieties with the same input practices 8. The Trademark Act, 1999 deals with the protection, registration and prevention of fraudulent use of trademarks. It also deals with the rights of
the holder of the trademark, penalties for infringement, remedies for the damaged as well as modes of transference of the trademark.
30 31